Clone sheep science has advanced, and reports of methods that cure aging have spread. Scientists have successfully extended the lives of numerous animals in preliminary trials, which may point to how humanity may reverse aging.
Age-Related Characteristics

In 1974. A strange phenomenon in the laboratory has been reported by scientists. Scientists cultivated cells in a petri dish, cells appear to divide only for a few days. Cells finally stop dividing and perish. There appeared to be some process that caused cells to age, and scientists eventually found what we now call the hallmarks of aging.
Mutation
Our cells must coexist with us for decades, during which time they may sustain harm. Our skin cells can be exposed to UV radiation and certain chemicals, which damage and modify the DNA over time. Permanent alterations in DNA are referred to as mutations. Depending on where the mutation occurs, the cell may be perfectly OK at times. However, mutations in genes required for survival may occur, and the cell may die as a result.
In other circumstances, mutations can alter the characteristics of cells, causing them to become malignant. As a result of mutations destroying critical genes over time, our cells operate less and less and we lose them. And this is one of your aging characteristics.
Mutations can occur when cells try to generate new cells after being exposed to radiation or certain substances. This is referred to as cell division. A cell must replicate its DNA for both cells to receive all of the genes required for cell division. However, DNA replication is not a faultless process and results in a few errors or irreversible mutations. The older the cells become and the more often they divide, the more mutations they might acquire during cell division. Not only that, but it also contributes to another sign of aging: telomere attrition.
Telomere Attrition
Telomeres are situated at the ends of chromosomes and are essential for chromosomal integrity. When a cell divides, its telomeres shorten; if telomeres get too short, the cell is harmed further. This is how aging wreaks havoc on our DNA. As we age, our mitochondria also cease to function.
Mitochondria
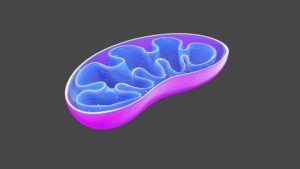
Mitochondria, commonly known as the cell’s powerhouse, are essential for providing humans with energy. In our cells, quality standards guarantee that our mitochondria remain undamaged and functional. These quality checks fail as humans age, implying that mitochondria have difficulty executing activities.
Because mitochondria no longer function correctly, the general metabolism of a cell has changed, resulting in a new set of problems. Everything begins with neck and back discomfort. Then we see the first grey hairs on our heads. We grow less active and develop an interest in board games. We lose more and more cells as a result of mutations and less intact mitochondria, which means our bodies are less rejuvenated and frailer. The cells that remain in our bodies are becoming less and less functional. This includes our immune system.
Read Also: Health Benefits of Swimming
Epigenetics Influence Genes

During the 1940s. Conrad Waddington, a physicist, was strolling through the town center of Cambridge, England. Waddington enrolled at Cambridge University to solve a single question. How do a few cells become a full organisms? All cells in our bodies are descended from a pair of identical embryonic stem cells. Embryonic stem cells are discovered early in development and can differentiate into muscle cells, brain cells, or skin cells.
Waddington’s Landscape
Waddington developed a model called Waddington’s landscape to explain how embryonic stem cells convert into adult cells. According to Waddington, whatever the method, embryonic stem cells can specialize in cells into a variety of cells, but once they pick what to become, they cannot change their minds.
A skin cell is always a skin cell. It took a long time for scientists to figure out how Waddington’s landscape worked. Although virtually all of the cells in our body share the same DNA, each cell has a unique collection of activated genes. Embryonic stem cells have activated stem cell genes early in development, whereas other genes are dormant. When an embryonic stem cell decides to become a muscle cell, it must deactivate its stem cell genes while activating muscle-specific genes. Epigenetics regulates the activity of genes.
Epigenetics implies that humans have processes that change DNA or the proteins that coat DNA, known as histones. In actuality, it’s more complicated, with more epigenetic layers, but for now, we’ll stick to DNA methylation and histone alterations.
When an embryonic stem cell decides to become a muscle cell, it can activate muscle-specific genes by removing DNA methylation marks and adding or deleting certain histone modifications. The stem cell gradually transforms into a muscle cell by changing DNA methylation and histone changes.
Epigenetics is vital not just for helping stem cells determine what to become but also governs aging. Loosing of mitochondrial genes reduces the mitochondria function correctly. However, humans do not generally lose these genes owing to mutations; rather, epigenetic processes inactivate them. In contrast, every genetic machinery in the cell requires chemicals from the mitochondria.
Epigenetic Alternations

At least three epigenetic alterations accumulate on a larger scale. It’s known as acetylation. Acetylation equals aging equals bad in this situation. These worldwide consequences help explain some of the markers of aging. But epigenetics has one advantage: it is reversible. We can make ourselves younger by removing or adding DNA methylation marks or histone changes.
Read Also: 14 Best Foods for Nervous System
Dietary Intervention to Reverse Aging

Special diets rich in whole foods and low in fat may aid in the prevention of age-related illnesses. This implies we are less likely to get heart disease or diabetes. For example, green tea, broccoli, sprouts, and soybeans have bioactive chemicals that have been proven to favorably alter the epigenetic landscape of malignancies.
There have also been some reports of calorie restriction and intermittent fasting having anti-ageing properties. Consume complete meals and veggies while avoiding fats.
Sports for Aging Reversal

Exercise has the potential to modify our epigenetic landscape and reverse aging. A study found that physical activity and a low BMI were associated with younger DNA methylation patterns.
This list also includes genes required for mitochondrial function. This makes sense because healthy mitochondria are essential for optimum activity, but it also has the potential to reverse aging. According to research, regular exercise links to longer telomere lengths in immune cells.
Read Also: The Health Benefits of Cycling
Stress Causes Cells to Age

Stress not only affects our daily lives, but it can also influence how we age. Chronic stress reduces life expectancy. Reduce stress by beginning yoga, creating a social support group, and going for daily walks. Stress ages your cells because it causes you to be more stressed, which causes your cells to age, which causes you to be even more agitated.
We’ve learned a lot about how cells age over the last few decades. Multiple variables appear to be involved in cellular aging, some of which are reversible. This implies that we may be able to reverse aging.
Read Also: Tips for Better Breathing
Can We Stop the Aging Process?

Probably not, but we may be on the verge of slowing down some of the markers of aging, making aging more comfortable overall.
